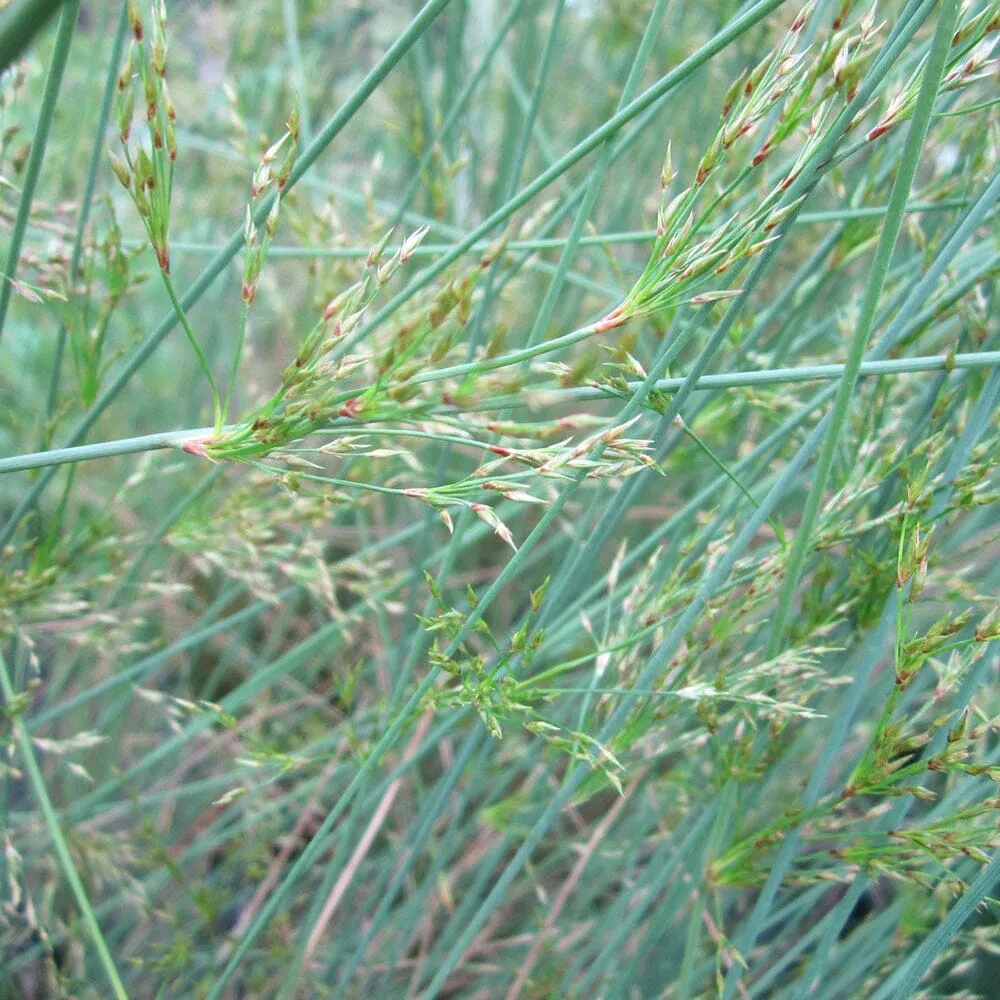
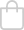
Juncus inflexus, commonly known as Hardstem Rush or Blue Rush, is a perennial grass-like plant that is native to Europe, Asia, and North Africa. It is characterized by its upright, rigid stems and blue-green foliage. Here's a detailed description and care guide for Juncus inflexus:
Description:
Juncus inflexus forms clumps of stiff, upright stems that can reach a height of 1 to 3 feet (30 to 90 cm). The stems are cylindrical and typically blue-green in color, providing an attractive contrast in gardens and landscapes. The foliage consists of narrow, linear leaves that grow in tufts along the stems. In late spring to early summer, small clusters of inconspicuous, brownish flowers may appear on the stems, but they are not the main ornamental feature of this plant. The overall growth habit is compact and dense, making Juncus inflexus suitable for borders, rock gardens, or as a low-maintenance groundcover.
Care Guide:
Lighting: Juncus inflexus thrives in full sun to partial shade. It can tolerate a range of light conditions but generally prefers at least 4 to 6 hours of direct sunlight per day. In hotter regions, providing afternoon shade can help prevent scorching of the foliage.
Water: Juncus inflexus prefers consistently moist to wet soil conditions. It is naturally found in wetland habitats, such as marshes, ponds, or along stream banks. Ensure the soil remains evenly moist throughout the growing season. Water deeply when the top inch of soil feels dry to the touch. In drier regions or during hot weather, providing supplemental irrigation can help maintain adequate moisture levels.
Soil: Juncus inflexus is adaptable to a range of soil types but prefers moist, loamy, or sandy soil that is well-draining. It can tolerate both acidic and alkaline soils. Incorporating organic matter, such as compost or well-rotted manure, into the soil before planting can improve its fertility and moisture retention capabilities.
Temperature: Juncus inflexus is hardy in USDA hardiness zones 4-9. It can tolerate a wide range of temperatures, from cold winters to hot summers. It is a resilient plant that can adapt to different climates.
Fertilizer: Juncus inflexus generally does not require heavy fertilization. It can obtain most of its nutrients from the surrounding soil. However, if the plant shows signs of nutrient deficiency or poor growth, you can apply a balanced, slow-release fertilizer in early spring. Follow the manufacturer's instructions for dosage and application methods.
Maintenance: Juncus inflexus is a low-maintenance plant. Regular maintenance involves removing any dead or yellowed stems to maintain a neat appearance. If the clumps become too dense or overcrowded, you can divide them every few years in early spring. Divisions can be replanted or shared with other areas of the garden.
Mulching: Applying a layer of organic mulch, such as shredded bark or compost, around the base of the plant can help conserve moisture, suppress weed growth, and regulate soil temperature. Mulching is particularly beneficial during the establishment period or in regions with extreme temperatures.
Pests and Diseases: Juncus inflexus is generally resistant to pests and diseases. However, it may occasionally attract aphids or be susceptible to root rot in waterlogged conditions. Monitor the plant for any signs of pests or diseases and take appropriate measures if necessary.
By following these care guidelines, you can enjoy the distinctive blue-green foliage and compact growth habit of Juncus inflexus in your garden. Adjust the care routine based on your specific growing conditions and monitor the plant for any signs of stress, pests, or diseases. With proper care, Juncus inflexus will provide an appealing texture and visual interest to your outdoor spaces.